Why Web Developers Should Learn SEO

You probably have one (or both) of these questions right now:
1 – what is SEO?
2 – why should I learn SEO if I am a web developer/freelancer?
By the end of this article, I hope to answer these questions and convince you of why web developers should learn SEO.
If you prefer watching, here's the video:
Let’s start with “what is SEO?”
SEO means ‘Search Engine Optimisation.’
In “simple English” it is creating or editing a website that Google can ‘read’ easily and your ultimate goal is to rank #1 for your search term (this is a simplified answer).
What makes me ‘qualified’ to talk about this topic?
My job for a large conglomerate was making sure that the company generates (a high) income each month through their websites.
I did this via various channels, but one of the main channels is SEO.
We had over a dozen (successful) websites and I have a few other clients that I handle SEO for as well as my own online projects.
SEO is broken down into 2 sections:
On-page SEO and off-page SEO.
On-page SEO happens within the website. It refers to all of the activities and optimising that you do on your website/page to raise the ranking in the search engine results.
Off-page SEO happens outside the website. It refers to all of the activities that you and others do for a website/page to rank higher in search engine results.
On-page SEO is generally a once-off fee, whereas off-page SEO is generally a recurring fee – more onto the importance of off-page SEO later and why this is relevant, but for now, let’s focus on on-page SEO (who knew I’d ever say “on-on” 8).
When developing websites, your primary focus should be ‘on-page SEO’.
In the case for this article, I will just be using SWD as a reference.
Example:
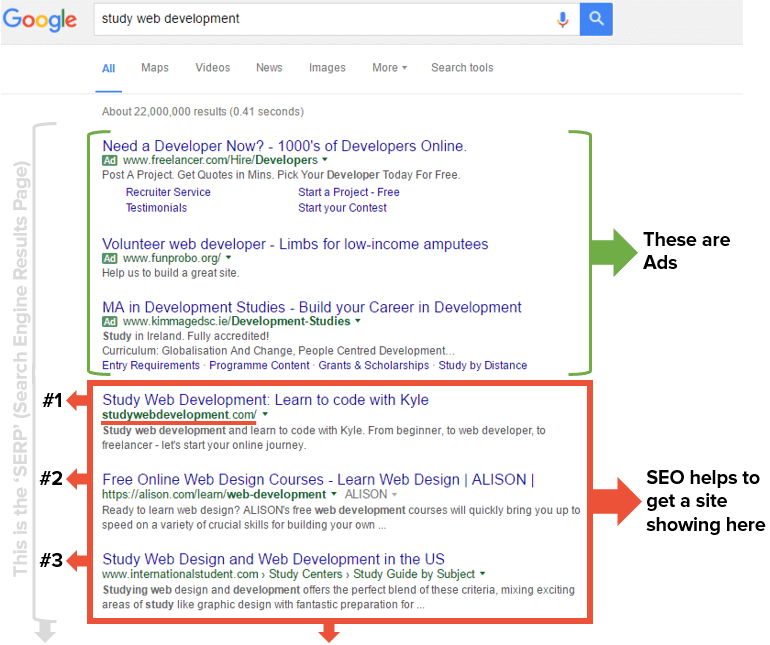
“Study web development” is one of the terms I aimed to rank for. I created my site in a way that I am now able to rank #1 for that term and other strategic terms.
The good thing about knowing (on-page) SEO is that you are able to charge for this service. Depending on how large the website is and the work required, I would charge anywhere between $200 - $800 for this basic SEO service (if it’s an ecommerce or a very large site, I’d charge much more) – you can charge whatever you feel this service is worth and whatever you feel the client would be willing to pay for it.
8 Quick On-Page SEO factors
Title
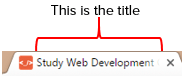
The title must be under 70 characters in length (aim for less than 60 characters). This needs to change on EVERY page.
Where possible, try and use the search term you want to rank for right at the beginning of the title tag.
The title needs to be relevant to your audience and it needs to explain what the page is about.
Click here to read some tips on how to create awesome titles.
Meta Description
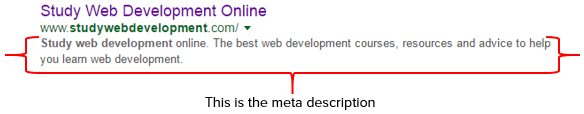
The meta description is only seen on the SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages) – as in the image above.
Meta Descriptions are not a formal ranking factor for SEO, it is definitely a ranking factor for conversions…
It must be under 156 characters in length and it needs to change on EVERY page. Make it relevant to the search term you want to rank for.
Read more about Meta Descriptions and their importance here.
URLs
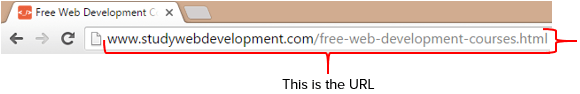
It’s important to create ‘SEO-friendly’ URLs (website link). Keep the URL as short as possible, but use the search term you want to rank for.
The URL needs to change and be relevant on EVERY page.
Images
I can’t tell you how many developers take the ‘easy-shortcut’ on this one.
You need to give EVERY SINGLE IMAGE an ALT Tag. Let me rephrase that better: You need to give EVERY SINGLE IMAGE an ‘SEO-friendly’ ALT Tag.
ALT Tags need to be structured like this:
alt=”web-development-and-beyond-ebook” (notice the hyphens – this is important as it indicates a ‘space’ in between the words).
Not only that, but when you SAVE the image in your folders, save it like you would save it as an ALT Tag. So the name of the image and the ALT Tag must basically be the same.
Favicon
A small, but underrated and neglected image for a website.
This is the image on the top left of the tab you are in on a browser.
![]()
Make sure you add a favicon to the site. If you’re like me (I’m a bit O-C-D) and you really don’t like seeing websites like this:
![]()
Then we will get along very well :)
But on a serious note, it doesn’t look professional and it ruins the whole site (maybe not, but just add it).
PS – this is not a ranking factor, but I just thought to add it in this list.
H Tags
H Tags show Google, “Hey Google, this ‘header-section’ of the site is important and the content on this page is related to my H Tag. I am giving it a H1/H2 tag so take note of it.”
Make sure you don’t overuse H Tags – use them sparingly and use your search term you want to rank for or at least a close synonym where possible.
You cannot use H Tags for paragraphs… It might not apply to you, but I’ve seen this happen very often.
Ideally, you want to use the H1 tag once as the main heading for the page. Then use H2 tags as the sub headings.
XML Sitemap
A sitemap is an XML document on your website’s server that basically lists each page on your website. Think of this as a ‘table of content’ for books, but just for a website.
It tells search engines when new pages have been added and how often to check back for changes on specific pages – all this helps Google read and understand your website better.
To create a sitemap is quite easy. Go to: www.XML-sitemaps.com and follow the straight forward steps.
Once you’ve created the XML document, submit it to Google Search Console (webmaster tools).
There you have it! Google should ‘scan’ your website within the 48 hours.
Side note: this doesn’t mean your site will now appear on the 1st/2nd/3rd… page of Google. It may take some time for that to happen and there are many factors involved but this is just a step in the right direction.
Fast Loading Time
Google mentioned that page loading speed is an SEO ranking signal.
A good page loading time is under 4 seconds. I almost made it ;)
To test your page loading speed, go to: GTMetrix.
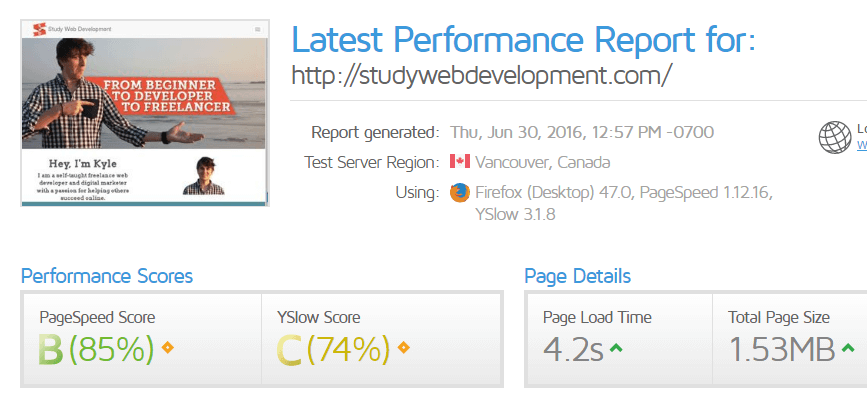
3 recommended ways to boost page loading speed is by using a CDN (Content Delivery Network), switching to a faster host like Bluehost or Dreamhost and compressing your images by using a service like TinyPNG.
Linking
This is split in two: Internal links and Outbound links.
Internal links are an underrated and often neglected ranking factor in my opinion. The logic is that if your website is a quality resource for others, wouldn’t it make sense that you’d link to previous articles you’ve written as well?
Wikipedia is great example of how to use internal links. They obviously use a lot, but they can get away with it. Depending on how long your article is, try and link to around 2-5 previous posts where possible.
Outbound links are links to related pages/websites that shows Google what your page/article is about. Put simply, by you linking to other pages on a certain topic, it’s a reflection on your site.
This is probably the #1 mistake out there. A good rule to follow is to try and use around 2-4 outbound links for every 1000 words.
When you link out, make sure to link out to authority websites (well-known websites) whenever possible.
Responsive Design
If your website isn’t mobile responsive yet, I definitely recommend you make it responsive.
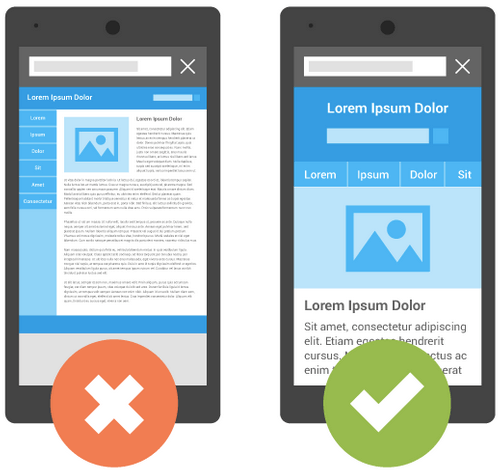
Source: Webmaster Central Blog
In 2015, Google started penalizing mobile unfriendly sites. I guess it’s only going to become even more important in the future. Take a look at these mobile trends here.
Google also prefers sites that are using responsive design.
I wrote an article on a few responsive frameworks you can use here. I personally prefer Bootstrap :)
3 Quick Off-Page SEO factors
Link building
Link building, overall, is the most important SEO ranking factor. This is a link from another website to your website/article which is basically a ‘vote’ that shows Google your site is of value because you are getting ‘votes’ from others.
After all, who links out to websites that suck? People link out to valuable content.
It’s important to note that it’s more about quality than quantity…
Let’s say you had a website that talks about a niche like JQuery.
Would you like referral links from 10 other websites also talking about JQuery or would you like links from 100 websites talking about Japanese flying squirrels?
Social bookmarking
Social bookmarking is bookmarking a link/article which is open to a community for people to store, organize, search, and share.
Notable sites for this are StumbleUpon, Digg and Delicious.
Social networking
It doesn’t need an explanation, but it’s important to be on social media and engage with your community. If done properly, it can really be a big contributor in traffic for a website.
Generally, just doing the above would be a good boost for a website. Of course there are MANY other factors and variables to consider (such as competitor analysis, site architecture, user experience, no-follows, content, bounce rate, dwell time, etc.)
This is in no way a full guide on SEO techniques. This is enough to get you started and you at least know enough to get paid for it.
Why Web Developers/
Freelancers Should Learn SEO
If you are a web developer working for an employer, what I have to say may not seem too convincing for you, but if you are a freelance developer, I hope you will read this next part with some thought.

“I’ve tried freelancing for a few months, but I didn’t have enough clients paying me so I had to go back to full-time employment.”
I’ve heard this MANY times from the SWD community and friends in this space.
It’s interesting though, because most of the time that I hear this, it is not a question of programming ability at all… almost every time the person has a very good programming knowledge.
So what could it be then?
I won’t be ignorant enough to try and point out the exact reason for others not being able to sustain their freelancing efforts, but I will try and mention 2 practical reasons of why this is an issue for many freelancers.
1 – the person does not know how to get more clients
2 – the person does not know how to provide additional services
“How to get more clients” deserves a full online course to get through :) so I will be focusing on point #2 for now.
Let’s face it; freelancing is not all ‘rosey’ and ‘perfect’ like some guys portray it to be. The truth is that if it were easy, everyone would be doing it right now…
The bottom line is freelancing (for the most part) does not provide a consistent, predictable monthly income like a full-time salary does.
One month you may feel like buying a penthouse, and the other month you may think you will be eating rice for breakfast, lunch and supper.
OK, that was a bad exaggeration, but you know what I mean :)
So what is the solution to this then?
It’s simple: a consistent, predictable income.
OK, that sounds all nice and makes me all fluffy inside, but how can this be done?
Well firstly, it’s not going to come out of thin air…
You need to have an additional service you can offer your existing clients, or you need to have an additional skill that you can use to get new clients.
That brings me to SEO.
If you learn SEO for 3 hours, once a day for up to 6 months, I can guarantee that you will feel like a pro at SEO and you will be able to charge for this service.
As I mentioned before, SEO is broken into 2 parts: on-page and off-page.
You can earn money by doing on-page SEO, but where the consistent, predictable income comes in is the off-page SEO.

I won’t go into specifics, but to sum it up, these are 4 things you could focus on:
Building targeted backlinks – you will be responsible for getting valuable links from other websites in the relevant niche of the business you are doing SEO for.
Infographics – great way to get links and get social shares. If you don’t know how to design it yourself, either learn how to design or outsource this task. Then learn how to market infographics.
Additional content – either you will write articles or you can hire others to write articles.
Guest blogging – you can gather a list of website owners and contact details relevant to the business niche you are doing SEO for, and contact them to get articles featured on their website.
If this sounds a bit strange to you, then good… it gives you something to research and learn about :)
You can easily receive a few hundred dollars up to a few thousand dollars per month for these services.
I’d like to end on this note:
The chances are, you will be creating websites/apps for businesses, right?
My question to you is what is the main aim of the website/app that you are creating for them?
In short, it will be to get the business more customers, which leads to more sales.
So then, what is the next logical question after this:
“How to get the customers?”
Now imagine if you had the skills to create the website AND be able to get targeted traffic (customers) to the website as well…
Think different, and remember that the greatest investment you can make is in yourself.
I recommend checking out Viperchill, Backlinko, Neil Patel and Kissmetrics to learn more about this topic.
 by Kyle Prinsloo Last updated Oct. 2, 2017
by Kyle Prinsloo Last updated Oct. 2, 2017